 Faraday's law of induction, also known as the flux rule, flux law, and Faraday–Lenz law, [19] states that the electromotive force (emf) around a closed circuit is equal to the negative rate of change of the magnetic flux through the circuit.
Faraday's law of induction, also known as the flux rule, flux law, and Faraday–Lenz law, [19] states that the electromotive force (emf) around a closed circuit is equal to the negative rate of change of the magnetic flux through the circuit.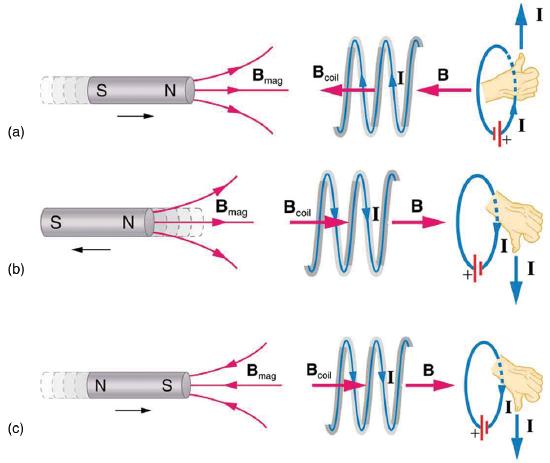 The equation for the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux is (23.5.1) e m f = N Δ Φ Δ t This relationship is known as Faraday's law of induction. The units for emf are volts, as is usual. The minus sign in Faraday’s law of induction is very important.
The equation for the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux is (23.5.1) e m f = N Δ Φ Δ t This relationship is known as Faraday's law of induction. The units for emf are volts, as is usual. The minus sign in Faraday’s law of induction is very important. Faraday’s law of induction clarifies how devices like transformers, motors, generators, and inductors function. Named after Michael Faraday, this law emerged from his experiments with a magnet and a coil, revealing that changes in magnetic flux through the coil induce an EMF.
Faraday’s law of induction clarifies how devices like transformers, motors, generators, and inductors function. Named after Michael Faraday, this law emerged from his experiments with a magnet and a coil, revealing that changes in magnetic flux through the coil induce an EMF.